CTs and PTs play a crucial role in modern power systems. CTs are used to measure current by reducing high currents to safe, measurable values, while PTs (also known as voltage transformers) help reduce high voltages to a safer level for accurate measurement. With the importance of these transformers in metering, protection, and control, proper testing is essential to maintain their performance and accuracy.
CT Testing Procedure
-
Visual Inspection: Conduct a thorough visual check for any physical damage, defects, or loose connections. Inspect for wear or environmental factors that could affect the performance of the transformer.
-
Secondary Circuit Verification: Before testing, verify the connections, including shorting and isolating links, to ensure proper grounding and functionality.
-
Insulation Resistance Test: Using a Megger, measure the insulation resistance between the CT windings and the ground, ensuring the CT is adequately isolated for safety.
-
Winding Resistance Measurement: Verify the resistance of both primary and secondary windings using a micro-ohmmeter, ensuring no shorts or damage within the windings.
-
Polarity Test: Test the CT’s polarity to ensure it is wired correctly, ensuring proper functionality in the system.
-
Ratio Test: Perform the ratio test by injecting current into the primary and measuring the corresponding secondary current to confirm the CT’s ratio.
-
Excitation (Saturation) Test: Gradually increase the voltage on the secondary winding to determine the CT’s saturation point, ensuring it operates effectively under high-current conditions.
-
Demagnetization: Apply a voltage above the knee-point voltage and gradually reduce it to zero to demagnetize the CT core and prevent residual magnetism from affecting future tests.
PT Testing Procedure
-
Visual Inspection: Inspect the VT (Voltage Transformer) for any physical damage, defects, or loose connections.
-
Neutral Grounding Verification: Confirm that the VT’s neutral is properly grounded to prevent safety risks during testing.
-
Winding Resistance Test: Measure the resistance of the VT windings to check for continuity and any internal issues.
-
Insulation Resistance Test: Use a Megger to measure the insulation resistance between the VT windings and the ground to prevent electrical faults.
-
Polarity Check: Verify the VT’s polarity by observing the voltage relationships between the primary and secondary terminals.
-
Ratio Check: Inject voltage into the primary winding and measure the corresponding secondary voltage to ensure the VT’s ratio is accurate.
-
Burden Test: Test the VT’s ability to handle the connected burden (load) without excessive voltage drop, ensuring optimal performance.
Testing Methods for Ratio: Current and Voltage Methods
Rui Du Mechanical and Electrical (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. explains two main methods for conducting the ratio test:
-
Ratio Test-Current Method: A suitable current, below saturation, is applied to the primary winding, and the secondary current is measured. The turns ratio is calculated as the ratio of primary current to the measured secondary current.
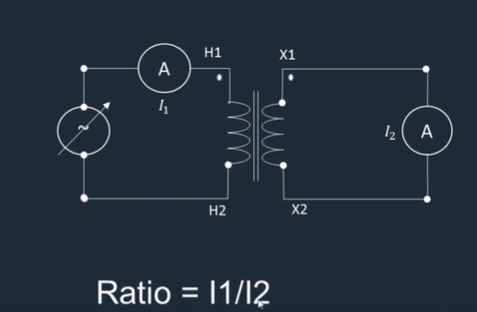
-
Ratio Test-Voltage Method: A suitable voltage is applied to the secondary winding, and the primary voltage is measured. The turns ratio is calculated as the ratio of the secondary voltage to the measured primary voltage.
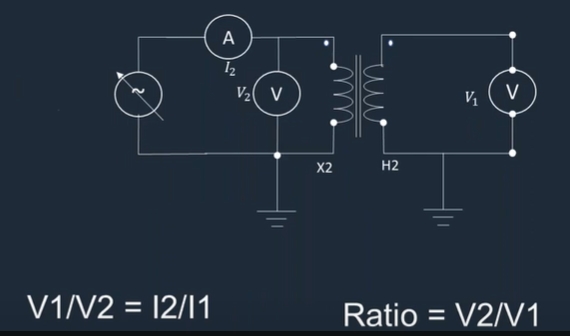
Accuracy Standards for Testing
-
For metering applications: +0.1% for ratio and +0.9mrad (3min) for phase angle.
-
For other applications: +1.2% for ratio and ±1 degree for phase angle.
The guide emphasizes that accurate CT and PT testing is crucial for power utilities, electrical safety, and system performance. With precise testing, utilities can ensure their equipment is properly calibrated and functioning, reducing the risk of energy loss or failure.
Click to find more Testing Procedure Details.
About Rui Du Mechanical and Electrical (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
Rui Du Mechanical and Electrical (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. is a leading manufacturer and supplier of high-quality electrical and mechanical equipment. The company specializes in producing current and potential transformers, as well as other power system components that ensure efficiency, safety, and reliability in modern electrical systems. With a commitment to innovation and excellence, Rui Du provides state-of-the-art products to clients worldwide.
For more information, visit www.wrindu.com
Media Contact
Company Name: Rui Du Mechanical and Electrical (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
Email: Send Email
Phone: 13661908522
Address:No.500 Jianyun Road, Pudong New Area, Shanghai
Country: China
Website: https://www.wrindu.com/








