Investors today have access to multiple sources to get information. Whether it's reports, macro data, analysts notes, alternative datasets, or even AI-generated forecasts, there’s no shortage of information. However the challenge isn’t access but filtering noise from actionable signals.
Where traditional forecasting is powerful and uses AI, it lacks the human validation part. For whom the products and services are made, if they don't agree or like it, what’s the point?
In comes prediction markets. Even though they put capital at risk, for investors and institutions, prediction markets provide solid signals towards the market trends, public opinion, and future demand. As the space grows, many organizations are also exploring prediction market software development to build structured platforms that can capture these insights at scale.
Let’s find out more about prediction markets vs traditional forecasting and which is better.
How Prediction Markets Generate Signals for Investors?
Prediction markets generate signals by converting future events into tradeable contracts through which people participate and share their opinion. Either with a Yes or No answer or by choosing the best option from several, these events allow people to buy and sell shares tied to specific outcomes.
The price of each contract is between $0 to $1 reflects the implied probability of the outcome that is yet to occur. For instance, if the contract trades at 0.65, this means the market is skewing towards this particular outcome and there’s a 65% chance it is likely to happen.
But are prediction markets accurate? Prediction markets are unlike forecasts or model outputs. Here the outcomes are backed by genuine public opinion and backed by capital at risk. The market forces ensure that greater public opinion pushes the price towards the likelihood of an outcome occurring and as new information emerges traders adjust their positions and the prices update in real-time.
The strength of this system lies in incentive alignment and rapid information aggregation. But its reliability depends heavily on liquidity, participant diversity, and resistance to manipulation. Thin markets can distort signals just as easily as flawed models.
What are the Limitations of Traditional Forecasting?
Traditional forecasting methods for investors have always been central to investment decisions. Especially when concerning macroeconomics, earnings modeling, valuation frameworks, or when they have to launch a product, build a new service, etc., these forecasts matter as they help identify the potential, understand the economics behind every decision, and more.
One of the constraints in traditional forecasting is the lag in updates or the lack of real-time information. Investors often look at institutional forecasts, which are built on fixed schedules and a limited amount of data.
This limits their understanding of the market and research areas, and in a fast-moving environment where trends change every day, access to real-time information is necessary. Another limitation of traditional forecasts is model rigidity and embedded bias.
Forecasting models are built on pre-established assumptions and calibrated parameters along with historical datasets. This pre-built structure provides analytical discipline, and this anchors the projections to past patterns. Hence, traditional forecasts are built on historical correlations.
But Predictions Markets are Not Infallible, There are Concerns
Prediction markets for investors offer incentive-based and real-time signals, but their reliability depends on the market type, your research goals, and the participation depth. These platforms have thin liquidity, which means in low-volume markets, the prices can move disproportionately, and when prices move, they will create distorted probability signals.
Similarly, in smaller markets, as we have seen in some markets on Polymarket, the risk of manipulation is higher because, due to limited participation, the markets can shift, sometimes even in the opposite direction. For businesses aiming to replicate such models with greater control and customization, a polymarket clone script can provide a faster route to launching a prediction marketplace.
Moreover, prediction markets are susceptible to herd behavior as the traders and participants are not immune to cognitive bias.
This bias can create sentiment-driven surges in the market opinion and temporarily override the accurate information-based outcomes.
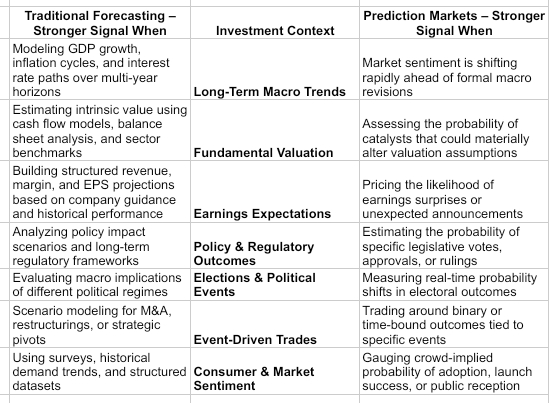
Is It Traditional Forecasting or Prediction Markets for Investors?
Conclusion
Between traditional forecasting vs prediction markets, the debate is less about which is superior and more about the signal design and accuracy. Where traditional forecasting offers structured depth and analytical prowess, prediction markets focus more on real-time signals. For institutions and operators looking to build robust, scalable prediction market ecosystems, TRUEPREDiCT provides structured deployment models designed for liquidity stability, compliance alignment, and production-ready performance.







