 Photo by Burst
Photo by BurstOriginally Posted On: https://islegitorscam.com/
The internet has changed virtually every aspect of our lives. Now, more and more things are done online, from meeting people, to making purchases, and more. As such there are literally millions of websites out there created to provide different online services.
However, the problem is that not all websites out there are legit. Some are fake websites operated by scam artists. These fake websites work in different ways but their ultimate goal is to rip off the unsuspecting – some steal your money outright, while others steal your sensitive data (with which they can proceed to steal your money).
However, the threat of being ripped off by scams in the internet should not make you stay clear of online services. There are just too many benefits of using online services! Thus, instead of allowing a fear of the scams to make you withdraw into the pre-internet age, it should rather make you embrace the internet, but with caution. That is, you should learn how to tell if a website is legit. That way, you’ll be equipped to easily sieve out the scams; and then, you can proceed to enjoy online services provided by legit websites.
That is where Is Legit or Scam comes in. It is a website that helps you to review online products and services and also investigates all their activities as well as listen to complaints and good feedback from users or customers through which we are able to confirm to you if they are legitimate or scam.
However, you can also learn how to find out yourself going through tips below.
This post helps by providing you with 12 ways which you can use in identifying a legit website.
1). The Address BarA modus operandi of the cyber criminals is to create a scam website that look exactly like a legit website. That way, persons who get to the page will think they are in the legit website; and any sensitive information (like log in details, credit card details, etc) put into the page is grabbed by the scam operators of the scam page. They can then proceed to use your details to access your accounts in the real website and “commit their evil”.
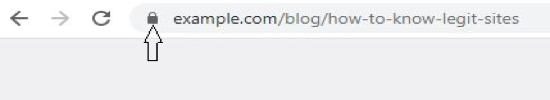
One way to tell a scam site that’s trying to present itself as a well-known legit site is by paying attention to the address bar of your browser. You’ll be surprised how many scam sites you’ll be able to identify from simply looking at the address bar. The address bar carries the URL. We’ll break down the URL into its components, so you know what exactly to look at when checking the address bar. The image below shows a typical URL, which is that of a webpage (how to know legit sites) in the website www.example.com.

Protocol
The first part of the URL is the Protocol; and that is where to start when checking a URL to determine a website’s legitimacy. Verify that the protocol is “Https” and not “Http”. The “s” in “https” means secure. This means that the communication between you and the website is encrypted and secure. That is, prying eyes are blocked off; and anyone who somehow manages to get a look in will see only scrambled data. But if the protocol is “http”, the communication channel is opening and anyone looking in can view whatever data you share while on the website.
Thus, if you’ll have to submit sensitive information in any website, you must ensure that the protocol is “https”. The popular browsers now give us a helping hand in knowing when on a secure connection. They do this with a padlock icon before the URL. Know that the operator of a website cannot affect this area of the address bar. Thus, a website cannot simply include the padlock icon to trick users that it is safe. The website has to actually use standard security certificates for it to earn the padlock icon. You can even click the padlock icon to view the digital certificate awarded to the website.
That said; the padlock icon and/ or the https protocol tell you that a connection is secure. However, that a connection is secure only means that unauthorized third parties will not steal your data. It does not mean that the website you are communicating with will not steal your data.
Domain
Another part of the URL that you should pay attention to is the domain. Very that you are in the right domain you intended landing in not some close imitation. If scammers want to target users of www.example.com, they may create a fake copy like www.examp1e.com (notice the replacing of the letter “l” with the number “1”). In the same “1” replacing “l” fashion, www.paypa1.com can be built to fake www.paypal.com. Also, www.amaz0n.com can be built to fake www.amazon.com; in this, the fake website has the number “0” (zero) where the legit website had the letter “o”.
Sub-domain
The sub-domain is where the ingenious scammers take their scam art to high levels. A sub domain can be thought of as a website in another website. Scam artist usually create sub-domains to mimic real domains. So users will be in a sub-domain of a fake website thinking they are in a primary domain of a legit website. Any sensitive information they submit while in the scam sub-domain is stolen; and you know the rest.
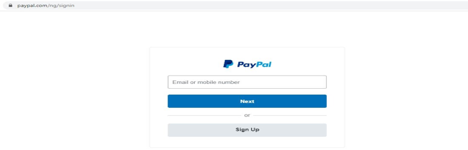
To illustrate this, consider the real PayPal page below:
Now consider the page below:
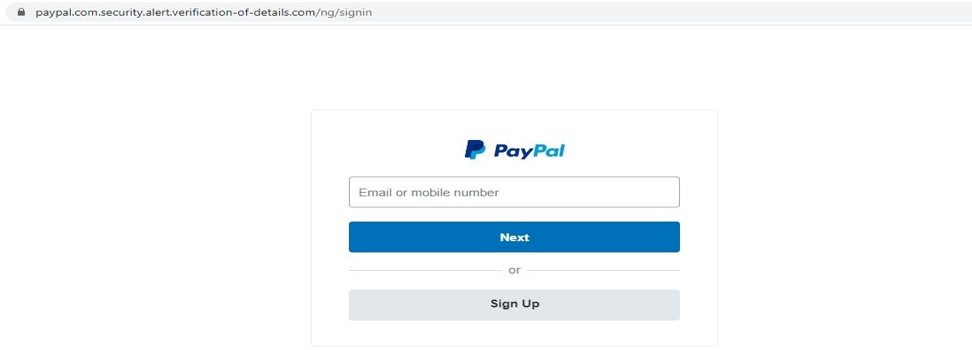
While both pages are exactly alike, the first one is the legit PayPal page, while the second one is simply a fake page designed simply to steal your PayPal login details. Without paying attention to the address bar, it is nigh impossible to tell that the second one is scam.
Now, look closely at the address bar – specifically the domain and subdomain. The domain is what comes before the TLD (.com/) while the sub-domain is what comes before the domain. So for the first URL that is www.paypal. com/ng/signin, it is clear that the domain is “PayPal”. Now consider the second URL that is www.paypal.com.security.alert.verification-of-details. com/ng/lognin; you’ll find that the domain (which is what comes before “.com/”) is “verification-of-details”. Everything that comes before it (www.paypal.com.security.alert) is just a sub-domain. Notice how the sub-domain starts with www.paypal.com to trick unsuspecting users that they are in the legit PayPal page. So if you enter your details in the second page, you’ll simply be submitting your sensitive information to a section of the scam website www.verification-of-details.com.
File Path
Another important thing to look out for when checking the address bar is that you are in the primary domain of your target website, and not in a web page of some scam website that is designed to mimic the real thing. The file path is whatever comes after the TLD; and it is simply a location of a file in a website.
Just as with the discussion above, scammers who want to target users of a particular site may create a scam website and make one page of the website an exact replica of the legit site whose users they want to trick. For example: consider the web page www.verification-of-details. com/excellentbank-login. If you are on the web page, you are simply on a page of the website www-verification-of-details. com. If the webpage is created to look exactly like the login page of excellentbank.com; then it is simply a scam site. The file path should give it away as a webpage of a scam website.
2). Domain OwnerAnother way to check that a website is legit is to look up the owner of the domain in online resources like Who Is (www.whois.com). Operators of websites must submit some registration information to the regulator of the domain name. In websites like WhoIs, you can check the person(s) behind any domain name (as well as their address and contact information). This information can easily help you tell if a website is legit. For example, if a website is presenting itself as one big brand, but the domain name check reveals that it is registered to one unknown quantity in some obscure address in another country, then it is probably a scam.
The Who Is check also reveals the address and telephone number of who owns the domain name. If these details do not correspond with information in the “contact us” page of the website, then all is not well.
3). Trust SealsAnother way of telling that a website is legit is the presence of trust seals. Legit sites are serious about giving their users confidence. As such, they submit to rigorous assessments by reputable security organizations; and online services that pass such checks are awarded the Trust Seals. Thus, a trust seal in a website tells you that the security system/ processes of the website pass the rigorous checks of the awarder. That said; a website with the trust seals (security certificates) of accredited and reputable security organizations is very likely legit.
However, don’t be fooled by the mere presence of security certificates in a website. Operators of scam sites know that people look out for trust seals in a website when checking that a website is legit, so some scam artists may actually put logos of reputable trust seals in their scam sites.
Thus, to check that a website is legit, go beyond checking to see trust seals/ security certificates. Verify the certificates. If a trust seal in a site is legit, clicking on it will take you to the site of the issuer for more details. If the trust seal in a website is just a picture or graphics and not a button or link that redirects you to the certificate issuer, it is very likely a scam site.
4). Licensing and RegulationIn some profession (like medicine), you’ll need a professional license so as to legally practice; and without such operating license, you are anything but legit. In the same vein, some online services will need to be officially licensed to operate. Examples of these are gambling houses like online casinos and sportsbook. The licensing authorities act as regulators that oversee the operation of the website.
That said; if the website you are checking out requires licensing but does not display any official operating license, then it is best to stay clear. It would mean that the website has not shown that it meets relevant operating standards; and that it is not regulated. However, where operating licenses are available, you can be sure the website is legit.
Just like the “trust seal” discussion above. Where simply finding an operating license in a website is not enough, it is important to verify this by clicking on the license and see if it redirects to the site of the licensing jurisdiction.
5). Physical PresenceMost often than not, scam services exist only in the virtual space. This is consciously done so that they can disappear without trace if their scam operation is discovered. Thus, an online service that has a robust physical presence is very likely to be legit.
To check for the physical presence of an online service, check the website for its registered address, then you can proceed to verify these using any of the address/ location verification resources on the web.
6). Contact InformationA sequel to “physical presence” is contact information. A feature of legit online services is customer satisfaction. Thus, legit websites will have different contact channels. So when checking that a website is legit, look for whether there are different ways for contacting the service provider (especially, the traditional channels like postal mail, email, live chat, and telephone service).
More importantly, test the contact channels. If an email address is provided, verify that it is not a generic one, but one with the company’s name. That is, if a company (EXAMPLE Ltd) operates a website (www.example. com); you know the website is more likely to be legit if the support email address is customer@example. com instead of customer@gmail com.
Also, if there is a telephone number listed for support; verify that it is a business telephone line and not a disposable mobile number. You can even go beyond simply checking for a telephone number to checking who uses it online, and more. There are many reverse phone number lookup services out there which you can use for this; these include: Who Calls Me (www.whocallsme.com), Unknown Phone (www.unknownphone.com), etc. When a live chat is featured, verify that you do not always get automated generic responses, but that there is a live agent that actually answers your questions.
7). Social Media PresenceSocial media is here to stay. Serious brands have social media accounts and publish online content regularly; reasons range from showcasing their industry knowledge and revealing their brand identity, to appealing to their clients and connecting with clients on a personal level.
That said; a high level of social media engagement (in such platforms as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, Pinterest, etc) is a sign that a website is legit. To check for the social media presence of a website, simply check that the social media accounts of the service are posted in the website.
However, know that the scam sites try their best to present themselves as legit. The scam sites know that people use social media links in determining a site’s legitimacy, so some of them put fake icons of social media platforms, which are simply graphics that do not link to real accounts. Thus, when checking a site’s social media presence, make sure to click on the featured social media icons to see if they actually link to real accounts. Also, know that, sometimes the scam sites do operate real social media accounts. However, most often than not these will be bare.
Thus, when determining the legitimacy of a website via its social media presence, go beyond checking to see icons of the social media platforms, go beyond clicking on the icons to see if they link to a real account. Also check for the level of engagement of the online service in its individual social media platforms. Read what real customers and followers of the service have to say on the platforms.
8). ReputationWhat others have to say about an online service is a good gauge of its legitimacy; especially if the “others” are real customers of the service and industry watchdogs.
Scam sites rip off unsuspecting customers; and persons who fall victim to such sites usually cry out in the independent customers’ review platforms. There are many of such sites where real customers of an online service share their honest experience; these include: Trustpilot, Reviews.io, Sitejabber, ConsumerAffairs, etc. It is usually not a good sign if you cannot find customer reviews of an online service anywhere. It is also not a good sign if the customer reviews of an online service is overridden with complaints.
What we call the industry watchdogs are independent reviews sites out there that provide honest and unbiased reviews of online services. Such independent reviews help users make informed decisions. Thus, before committing to an online service, it is wise to check that it is recommended by third party review sites.
9). Overly attractive OffersThe good old fashion fraud tactic is to dangle attractive offers before unsuspecting users. Many users have caught up with this tactic, but some still fall prey. If an offer is too good to be true, it probably is. So the next time you see a website advertising a new-model smart watch (or some other high-tech gadgets) for $10; you really do not need a scam seer to whisper into your ears that you are very likely facing a scam website.
If you fill those forms to send in the money, chances are that the money will go, but that the gadget will never be received. It could even be worse; some scams will simply use the really low offer to lure you into submitting your payment card information, after which they’ll proceed to clear your account.
10). Legit Payment MethodsWhen dealing with e-commerce sites, you should verify that the website use legit payment methods, especially those with protection mechanisms. For example, if a website pulls the “too good to be true” scam on you, and you unfortunately fall prey; you can get back your money if the payment was made through methods like credit cards, and PayPal. Also, if information-stealing scam sites somehow steal your bank information, and then proceed to make unauthorized transfers from your account; you’ll be able to get back you money.
That said; you know things are not right if an e-commerce website only accepts payment methods that lack buyer protection mechanisms. So the next time you can only make payments via Western Union transfers or gift cards, think twice.
However, that an ecommerce site uses payment methods with buyer protection does not necessarily mean it is legit. Buyer protection usually time requirement. That is, you can only get your money back if you file the chargeback within a particular timeframe from the transaction time.
Knowing this some scam sites allow legitimate payment methods with protection mechanisms, but they employ policies (or tactics) that string you along until the time (for filing the chargeback) has elapsed. Thus, if an e-commerce website has policies that serve to delay the contesting of a payment with your financial institution, it is very likely not legit.
11). Pay Attention to the ContentAnother way to tell that a website is legit is by paying attention to the content of the website. Legit websites have a responsible team with oversight over whatever is published in the website. Thus, content of their website will meet certain quality standards.
That said; a website with a lot of spelling errors and grammatical blunders is at best fishy. True, the legit website will have the occasional typo here and there; but the website will still be professional presented.
12). Google Safe Browsing Transparency ReportThere is a reason Google is a leader in online services. Working for a safer web, Google has developed a simple tool for checking that a website is legit – the Google Safe Browsing Transparency Report. If you want to check the legitimacy of a website, simply copy and paste its URL into the search bar in the Google Transparency Report page (https://transparencyreport.google.com/safe-browsing/search).
It is not only outright scam sites that this resource detects; it also detects legit sites that have been compromised by hackers.

